Wastewater treatment for sewage treatment facility and water purification plant, and case studies

Treated water is disinfected and discharged into public waters or reused as industrial water or other non-potable water.
In order to protect the aquatic environment, such as rivers and oceans, sewage treatment plants must properly manage water quality.
We have an important role to play in protecting the water environment by using water and sewage correctly and reducing the burden on sewer pipes and sewage treatment plants.

As of 2006, there were approximately 2,000 sewage treatment plants in operation in Japan, with an annual treatment capacity of approximately 14.1 billion tons (equivalent to about 11,320 cups of Tokyo Dome) (data from the Japan Sewage Works Association).
Sewage treatment plants are constructed and operated with the main purpose of purifying rainwater and sewage. Purification mainly refers to the process of removing organic matter from sewage, which involves physical and biological treatment.
Wastewater treatment methods for sewage treatment facility and water purification plant, etc.
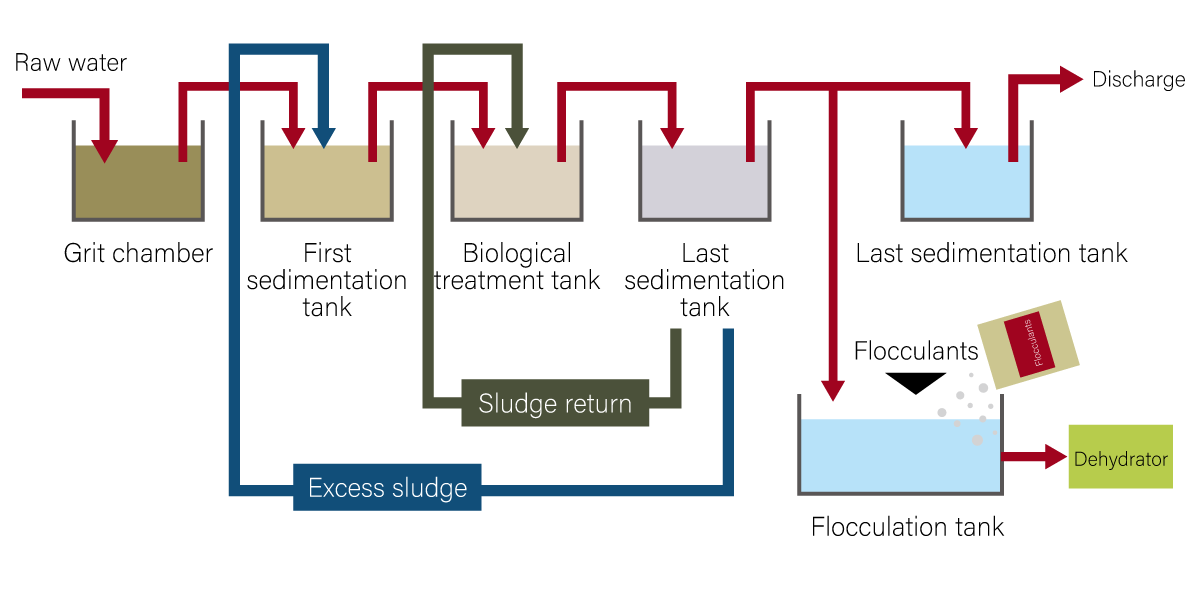
【Sewage】
Sewage includes human waste from flush toilets, domestic wastewater from cooking and laundry at home, and industrial wastewater (excluding farming) from business establishments ranging from stores, hotels, and small factories to large factories.
【Treated water】
Physical treatment includes sedimentation tanks to separate and remove sedimentable organic matter from sewage, and flotation and filtration.
In biological treatment, dissolved and suspended organic matter in sewage is fed to cultured microorganisms, which oxidize and decompose it into water and carbon dioxide gas, etc. The activated sludge method is a typical example.
It is used as a secondary treatment process in most treatment plants.
【Water resources】
In addition, chemical treatment, such as disinfection, is performed before the final discharge.
Treated water that has been purified through the treatment process is disinfected and discharged into public waters or reused as industrial water or other non-potable water.
In large cities where groundwater sources are difficult to access, highly treated water, which is superior to surface water in terms of quality, is an important water resource.
In addition, the water is used for river maintenance, landscaping, fire prevention, snow suppression, irrigation, and other purposes.
【Examples of chemical use】
※Since a large amount of organic sludge is generated during the sewage purification process, a sludge treatment process is required to reduce the volume and dispose of this sludge in a sanitary manner.
Concentrated sludge is generally in the form of muddy water with a water content of 95% or more, and is dewatered to reduce its water content to 85% or less.
※Dewatering is performed by forming flocs in concentrated sludge and then separating the water with a dewatering machine that uses centrifugal force, filtration, or compression.
The chemicals used are inorganic coagulants and polymer flocculants, and it is important to select and add the appropriate chemicals and concentration to form flocs suitable for the dewatering machine.



